What's ESLint?
ESLint is the best JavaScript syntax checker.
It can locate hundreds of common mistakes, enforce your preferred coding style (spaces not tabs!), and is infinitely configurable.
Unlike other tools, ESLint also understands ES6+ syntax, which means you can use it on next-generation JavaScript.
Enabling ESLint
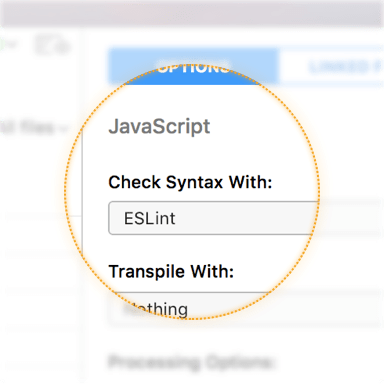
Select a JavaScript file, then choose ESLint from the Check Syntax With pop-up button in the Inspector Pane.
Alternately, to enable ESLint for all JavaScript files at once, open Project Settings, choose the JavaScript category, and use the same pop-up button.
Syntax Issues
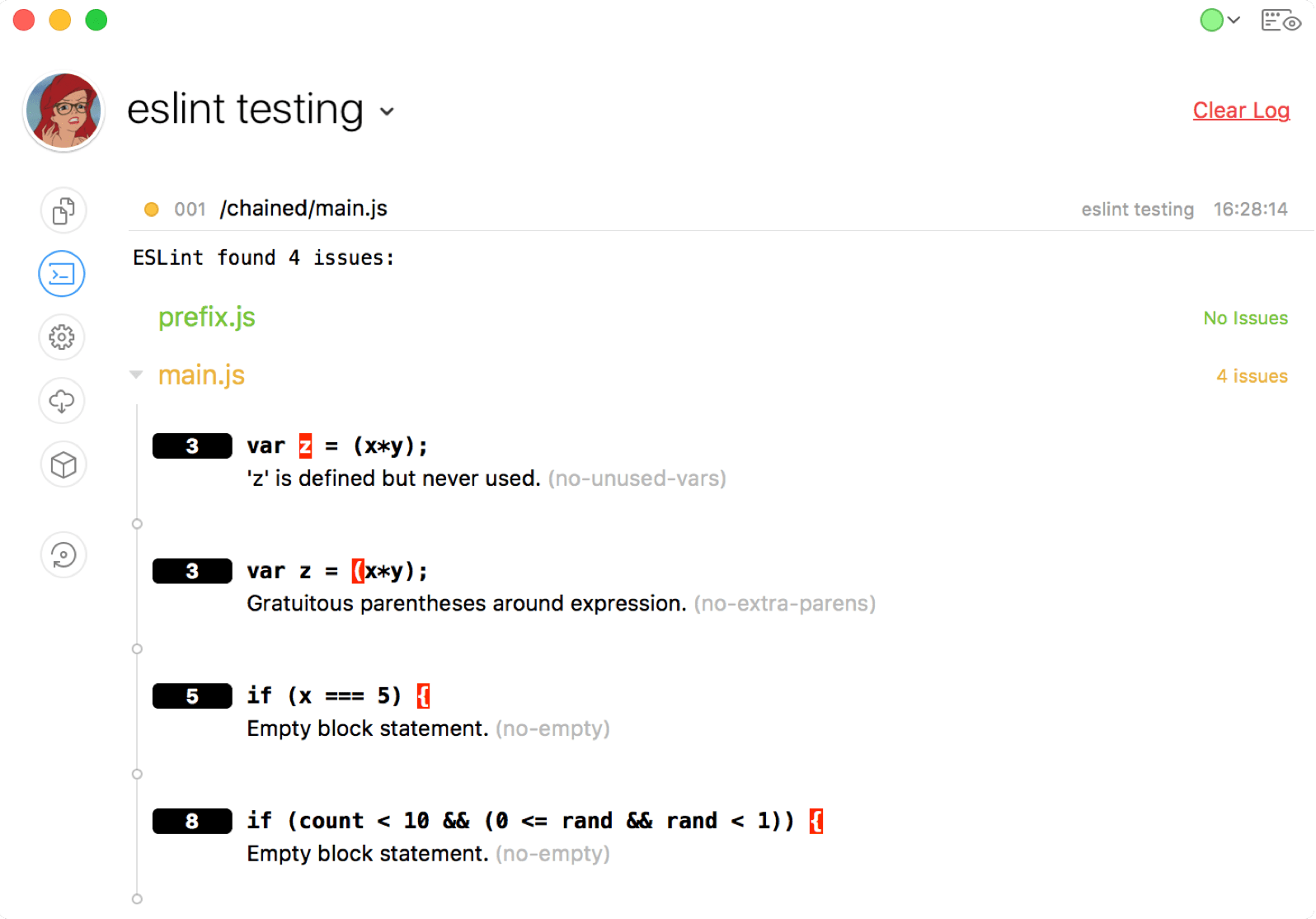
When problems are found in a file, they appear in CodeKit's log:

The line number of the issue appears in the black rectangle. The character where the problem starts is highlighted in red. The name of the ESLint rule that triggered the warning is shown in grey, after the warning itself.
Collapsible
Log entries in CodeKit are collapsible. Click the main log entry to expand or collapse detailed information, including syntax issues.
Linked Files
CodeKit lets you combine JavaScript files. When the base file (the one that imports others) is processed, the whole chain is syntax-checked at once. This means, for example, that a variable declared in an imported file will not be "undefined" when it's used in the base file.
Issues are separated by file. Here, main.js imports prefix.js:
Skipping Issues In Imported Files
You can tell CodeKit to ignore issues in an imported file. Select the base JavaScript file, then choose the Linked Files section of the Inspector:
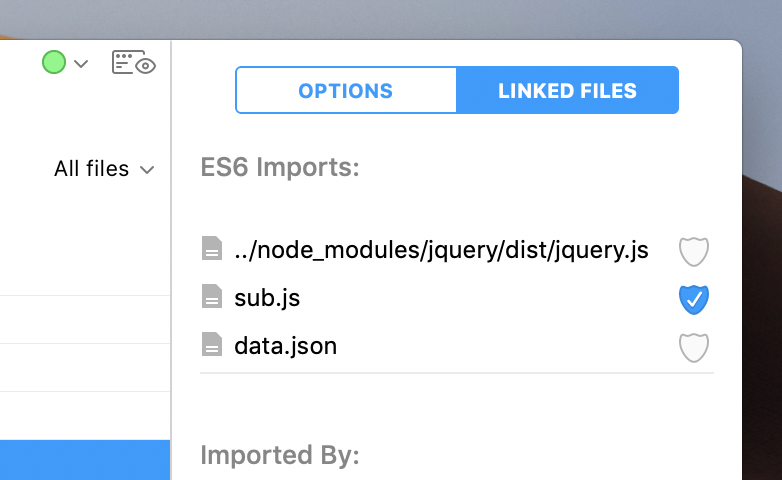
Uncheck the Shield Checkbox next to the file you want to skip. CodeKit will no longer scan for issues in that imported file nor any files it imports.
Note: If you import a file in a bower_components or node_modules folder, the Shield Checkbox is automatically unchecked for that file.
Pro-Tip: If you add //quiet to the end of your import statement, CodeKit will automatically uncheck the shield:
import {thing} from "./other.js" // quiet
// "other.js" will be skipped during syntax-checking
Configuring ESLint
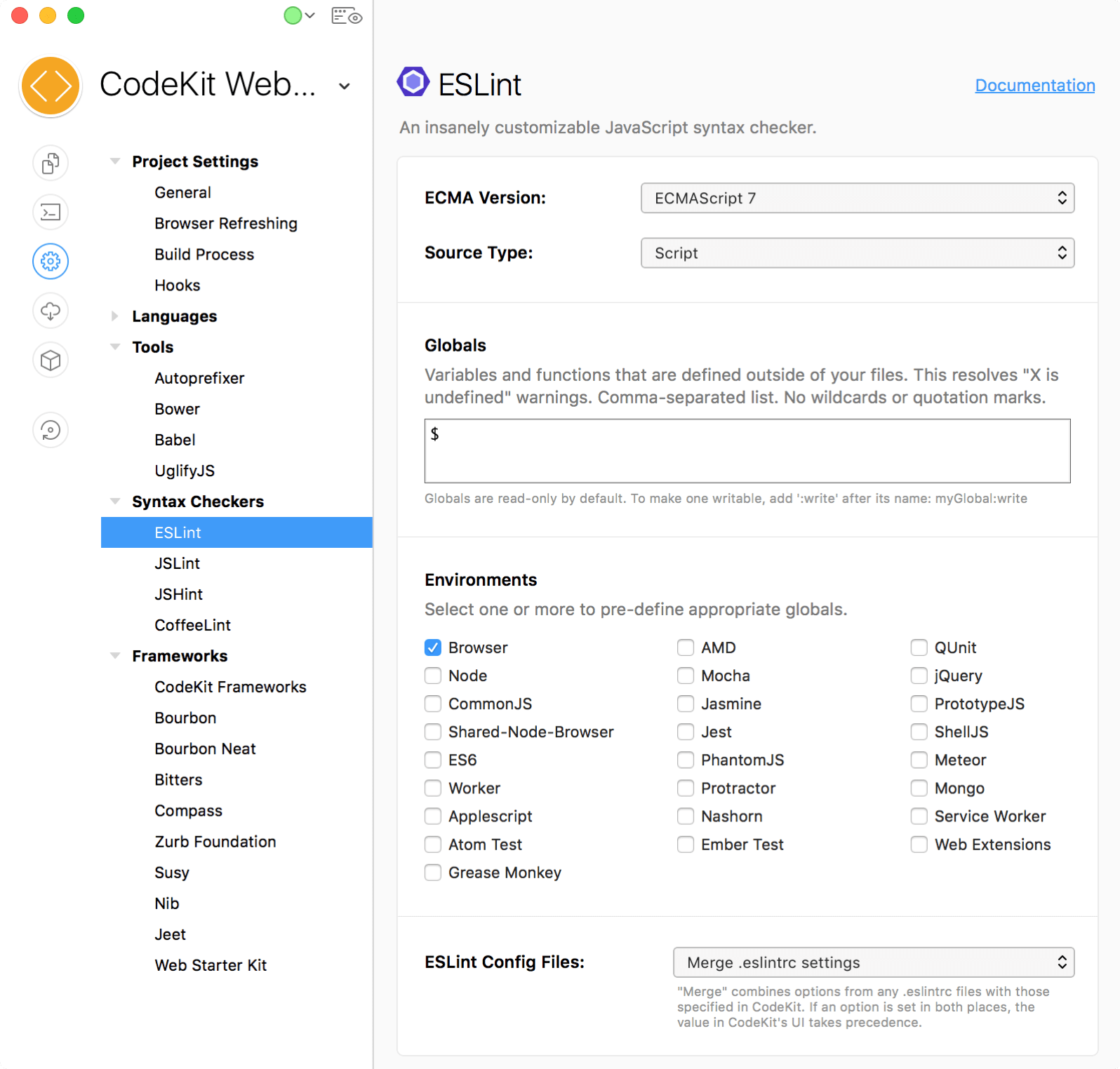
Open Project Settings, then choose the ESLint category under Syntax Checkers:
ECMA Version
This defines which version of JavaScript your code targets. The default is ECMAScript 7, which includes ES2015 syntax. If you set this to an older version of ECMA and attempt to use newer language syntax, ESLint will throw a parsing error.
Globals
ESLint may warn about "undefined" variables and functions in your code. If those items are defined outside of your script, add them to this field to eliminate the warnings.
By default, Globals are read-only. If your script attempts to write a value to a Global, you'll be warned. To eliminate that warning, add :write after the global's name.
Environments
Check the environments where your script runs and ESLint will automatically include Globals appropriate for that environment. For example, when Browser is checked, the console.log() function will not produce a "console is undefined" warning.
ESLint Rules
To control what ESLint considers a syntax error, you enable specific rules. The master list of rules is on ESLint's website. CodeKit includes every rule, organized into the same sections:
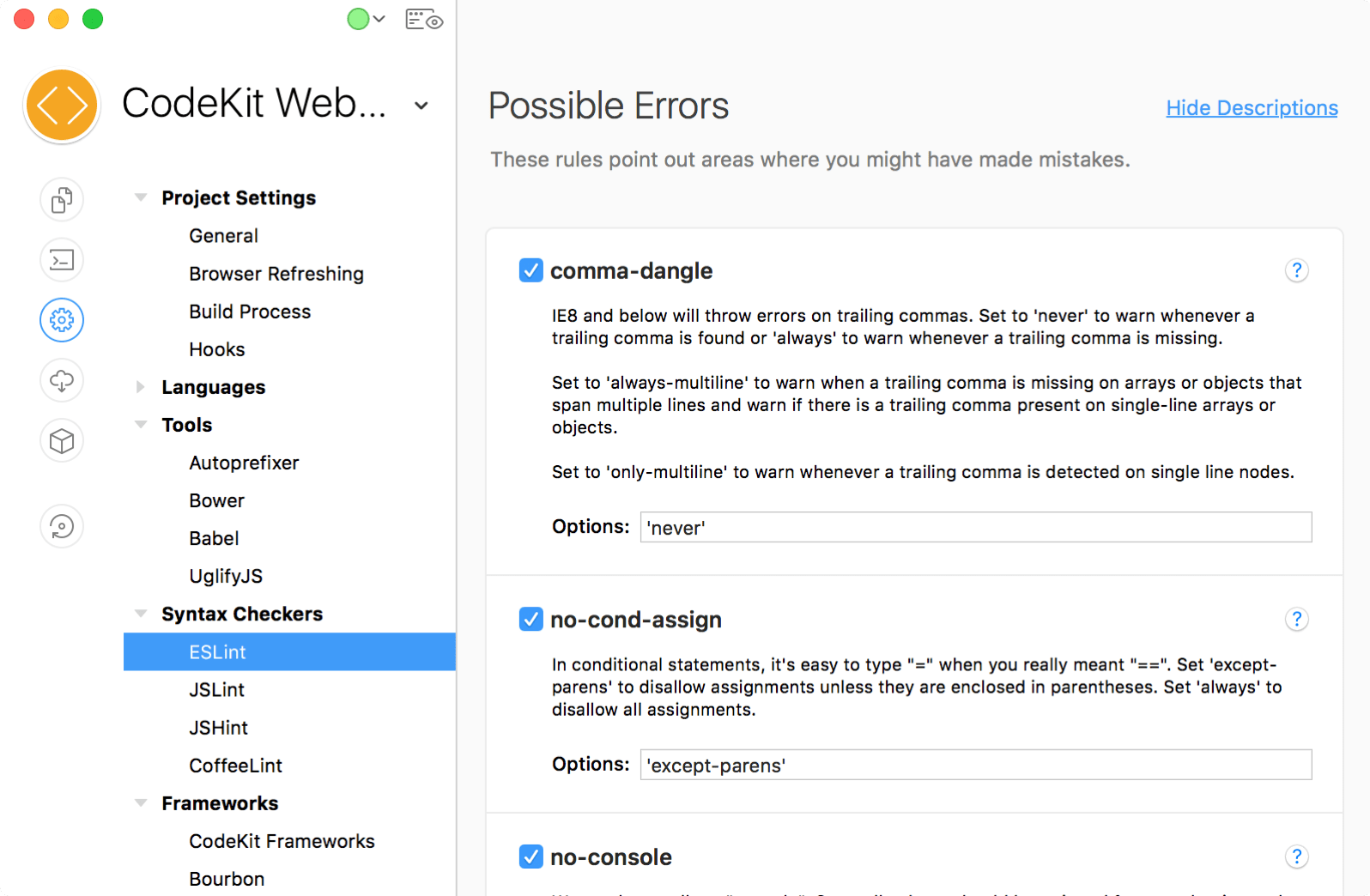
To enable a rule, simply check the box next to its name.
Rule Options
Some rules have options. You control these by setting specific strings in the Options text field for each Rule.
Warning: The syntax that ESLint expects for an option varies from rule to rule. Some are simple strings. Some are JSON-style objects or arrays. Before you change an option string, be sure to read the documentation for the associated rule. An incorrect entry or typo will cause ESLint to fail.
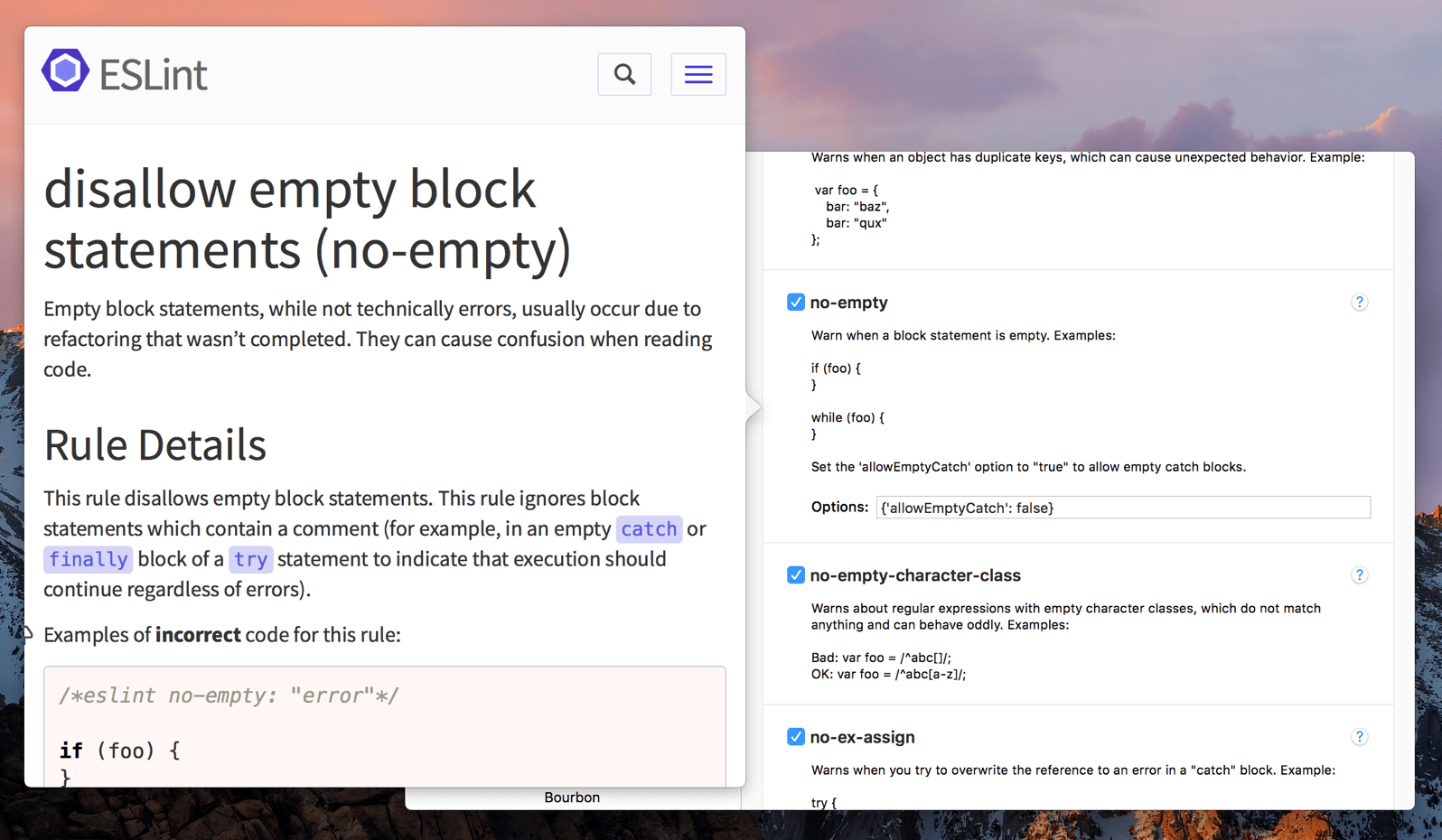
Rule Documentation
Click the Question Mark button to instantly view a rule's documentation in a popover:
Configure Once
You probably don't want to customize ESLint every time you start a new Project. You don't have to. Read Defaults For New Projects.